
Streamline Your Hiring Process: The Best HR Software for Startups
Get equipped with insights on selecting the right HR software for startups, including tips for successful implementation.
Today’s supply chains are facing significant pressure.
Major disruptions, port bottlenecks, extreme weather, and shortages in both supply and labor have become the norm, leading to shipping delays.
While some events are unexpected and beyond industry control, many common supply chain issues stem from poor distribution management.
In hopes of creating more resilient and efficient supply chain channels, companies are shifting from manual processes to analytics and AI-driven platforms. Distribution management software is a key player in this transition, offering real-time data, handling repetitive tasks, and streamlining logistics.
In this article, we explore what distribution management systems are, their impact on businesses, and whether their future lies in automation.
Distribution management involves managing the flow of goods from producers to the marketplace. It is a function with many sub-functions, including packaging, storage, inventory control, and coordinating logistics and supply chains.
Consider a clothing retailer that needs to manage the distribution of fashion items from global manufacturers to its various store locations.
With efficient distribution management, the company can ensure that seasonal clothing such as winter coats or summer dresses arrives on time, is properly inventoried, and distributed to stores based on regional weather patterns and customer demand.
For these reasons, distribution management is crucial for companies as it affects their ability to sell products quickly, maintain competitive pricing, and meet customer expectations.
Today’s distribution management goes beyond just transporting goods from one place to another. It involves collecting and sharing crucial information that helps identify growth opportunities and enhance market competitiveness.
So, what exactly is a distribution management system?
Simply put, a distribution management system (DMS) is a software-based solution that optimizes the workflow and process of distributing goods.
Effectively using these data analytics tools provides companies with valuable insights throughout the supply chain, by improving demand forecasting and enabling better data sharing with partners.
Take for example 7-Eleven, which announced a revamp of its US stores by replacing its outdated twice-weekly delivery system. Inspired by their advanced Japanese operations, they will now use a sophisticated DMS to make daily fresh food deliveries.
Moreover, orders to each store will be customized based on sales data, demographic trends, and local weather forecasts, ensuring optimal stock for each location.
Undoubtedly, the future of distribution depends on adopting advanced distribution management systems (DMS) to gather market intelligence and streamline logistics efficiently.
Though each organization takes a unique approach to distribution management, all managers should consider some crucial elements:
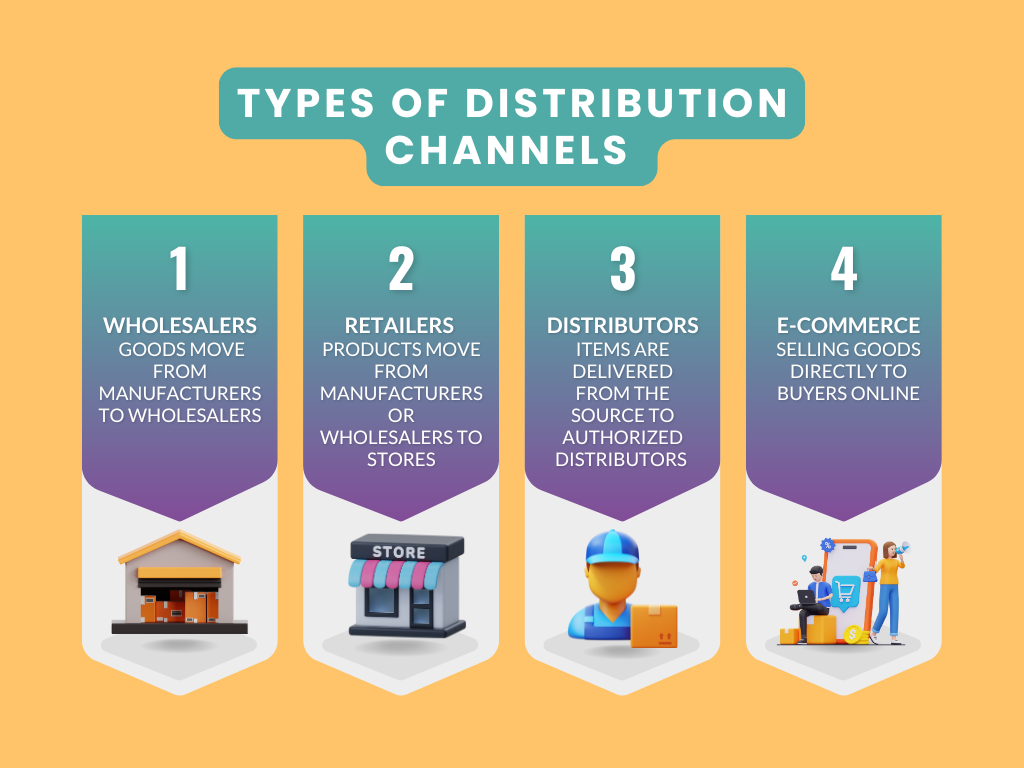
A distribution channel is the network through which a product travels from its origin to the consumer.
Historically, there were three main channels:
E-commerce, the newest and most disruptive channel, involves goods sold directly to buyers online, causing significant changes in traditional distribution strategies.
While distribution management is focused on moving goods from manufacturers to consumers, logistics management covers a broader range, including the planning, implementation, and control of the flow and storage of goods, services, and information from their origin to consumption.
Logistics and transportation can vary widely among industries because of different supply chain structures, product characteristics, customer demands, and regulatory requirements.
For example, the food and pharmaceutical industries emphasize speedy and temperature-controlled transportation, whereas sectors dealing with durable goods prioritize inventory management and after-sales service.
Optimizing transportation routes and modes to reduce transit times, cut fuel consumption, and lower carbon emissions are vital for distribution management.
Inventory management involves overseeing, controlling, and organizing a company’s stock of goods.
It includes tracking the quantity, location, and status of various business items, such as raw materials, work-in-progress products, and finished goods. Once inventory is received, it must be monitored to ensure sufficient supply to meet demand.
In other words, decisions about what to stock, where, and how much to stock are essential for smooth distribution operations.
According to data, 24% of small businesses still track their inventory with pen and paper.
However, the business world constantly evolves, and technology plays a significant role in this transformation. With advancements in AI and new analytics models, companies that rely on outdated methods risk falling behind their competitors.
Affirming that notion is a statistic from a recent MHI and Deloitte report, revealing that 55% of supply chain executives are boosting their investments in supply chain technology and innovation. Among them, 88% anticipate spending over $1 million, while 42% expect to invest more than $10 million.
The right software and digital tools can improve the supply chain and streamline an organization’s existing workflows.
For these reasons, investing in distribution management software and automation tools is essential for modern businesses.

Remember the headlines about shortages of everything from PlayStations to medical devices during the supply chain crisis a few years ago?
While these shortages are no longer daily news, the pandemic exposed many vulnerabilities and underscored the importance of an efficient distribution process.
A smooth distribution process significantly affects business operations, affecting everything from cost efficiency to customer satisfaction.
According to McKinsey, companies with effective distribution management can achieve up to 15% higher profitability. How does this happen?
Increased sales can boost profit, which benefit from high and consistent service levels. A well-managed distribution process meets customer demands and builds trust and loyalty in the brand.
When customers receive their products on time and in full, satisfaction increases, leading to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth. High service levels can also differentiate a company from its competitors, attracting more customers and increasing sales.
On the cost side, efficient logistics operations can lead to significant savings. For example:
Attitudes towards distribution have shifted over the years. Previously, logistics was often seen as an added expense for companies selling products.
However, it now we understand that while there are costs involved in moving and storing goods, distribution and logistics add significant value to a product.
Last year, Amazon hired 250,000 employees for the holidays to ensure orders were delivered on time.
While big retailers can afford to bring in such a large seasonal workforce, how can a small online retailer scale up to meet increased demand during the peak season without delays or errors in delivery?
The answer is simple: by efficiently planning their distribution management process.
Streamlined logistics and optimized inventory management allow businesses to meet increasing demand without compromising delivery speed or product quality.
For instance, automated inventory tracking, optimized shipping routes, and predicting market seasonality by keeping historical data can help small retailers manage any changes in demand.
One significant risk in distribution management is the lack of visibility into stock levels across multiple locations or distribution centers. Companies may struggle to maintain optimal stock levels without accurate, real-time data on inventory levels.
Too much inventory can tie up capital and increase storage and carrying costs while running out of stock can result in missed sales and unhappy customers.
Additionally, a DMS makes adopting and managing a diversified supplier base strategy easier, reducing supply chain disruptions risk.
By sourcing globally, businesses can stay flexible and adapt to unexpected events, like natural disasters and geopolitical instabilities, which often affect the supply chain.
Organizations should invest in advanced inventory management systems that provide real-time visibility and analytics to avoid these risks.
While it’s best to customize management systems to meet specific organizational needs, consider these general strategies to improve your workflows:
With growing global warming and overconsumption concerns, companies must reconsider their distribution management strategies.
Today, supply chain companies face mounting pressure to become more environmentally responsible and sustainable.
According to a recent survey, almost half of the respondents (48%) report increased pressure to adopt sustainable practices.
This pressure comes from consumers, regulators, industry groups, social media, and other stakeholders who expect brands and their supply chains to meet high environmental standards.
Current sustainability efforts focus on several key areas: electrification (40%), natural resource management (29%), water usage (27%), renewable energy (27%), and Scope 3 emissions, which are indirect emissions that the company is responsible for (23%).
By leveraging advanced technologies and adopting sustainable initiatives, businesses can navigate the complexities of today’s supply chains and drive long-term success.
Senior Content Writer at Shortlister
Browse our curated list of vendors to find the best solution for your needs.
Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest trends, expert tips, and workplace insights!

Get equipped with insights on selecting the right HR software for startups, including tips for successful implementation.

Explore how HRIS streamlines HR operations while at the same time improving employee engagement, compliance, and organizational efficiency.

Explore the transformative influence of BI solutions on contemporary business strategies.

Explore free genealogy software solutions and their helpful features to discover more about your family roots and ethnicity.
Used by most of the top employee benefits consultants in the US, Shortlister is where you can find, research and select HR and benefits vendors for your clients.
Shortlister helps you reach your ideal prospects. Claim your free account to control your message and receive employer, consultant and health plan leads.